Sustainable orthopaedic surgery residency training in East Africa: A 10-year experience in Kenya
Abstract: Low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) have continued to lag behind high-income countries in all measurable outcomes of health care. As concluded by the World Health Organization during the 2013 Global Forum on Human Resources for Health, an adequate healthcare workforce is mandatory to provide universal health coverage. Despite efforts to increase the numbers of healthcare workers, an extreme deficit in highly trained surgeons remains.
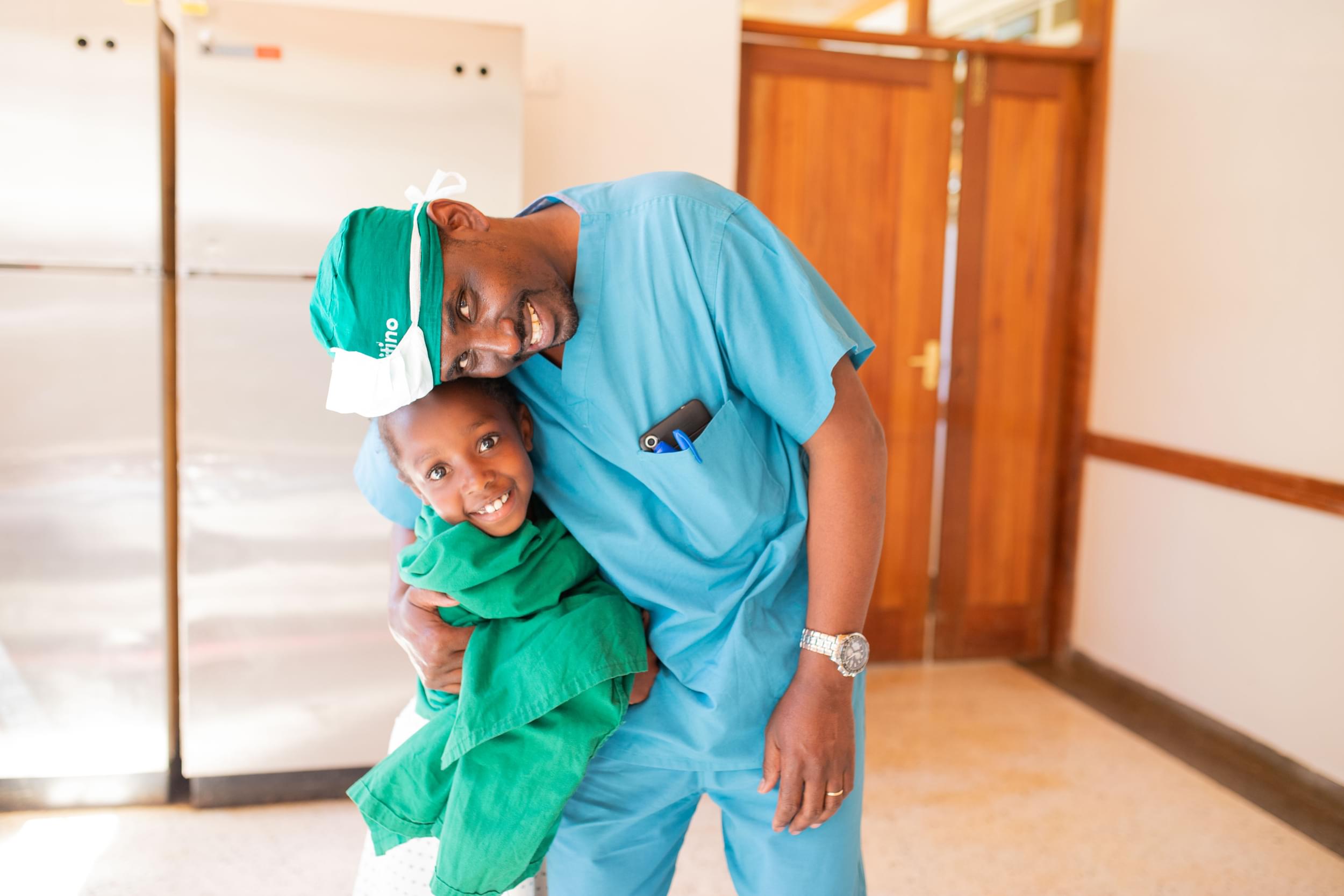
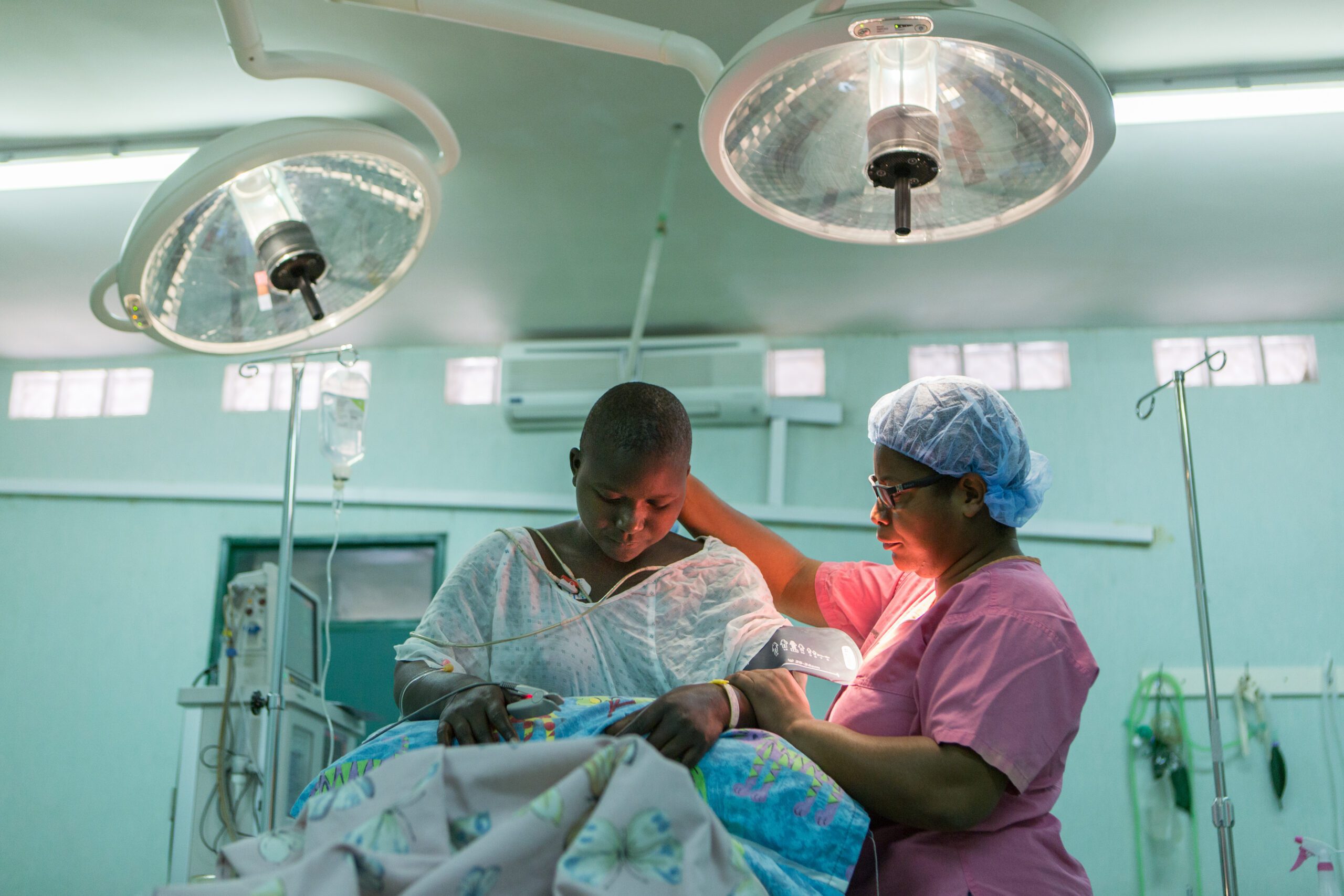
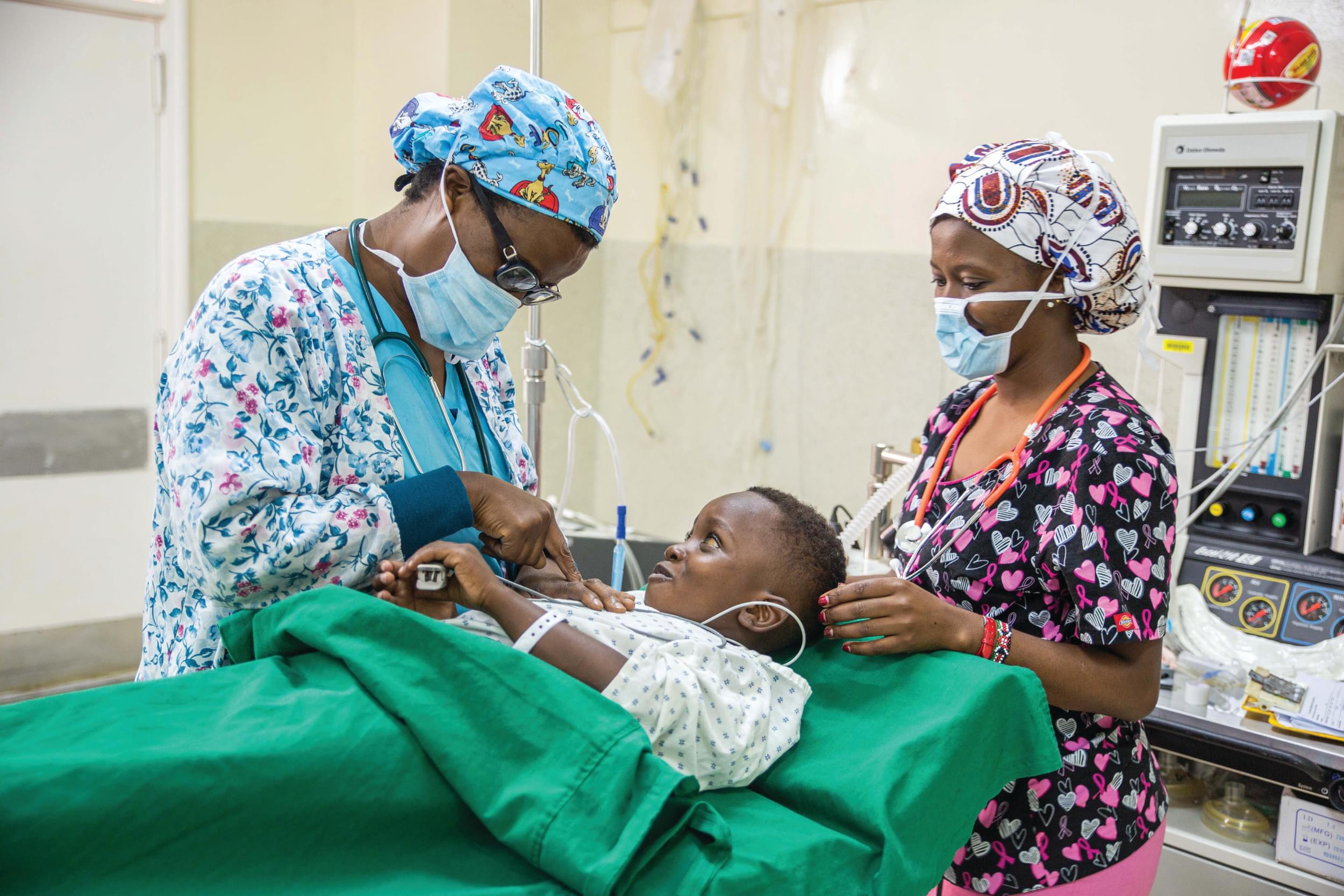
Several options exist to provide training for surgeons in LMICs, including local training by local surgeons, sending local surgeons abroad for training, or local training by short-term or long-term visiting surgeons from high-income countries. This article further discusses the benefits and challenges of each option and reviews the 10-year outcomes of the Orthopaedic Surgery Residency Program at the CURE Kenya Hospital in Kijabe, Kenya. The program has graduated nine orthopaedic surgeons who are all practicing in Africa, five of which are full-time attending consultants in residency training programs. An additional eight residents are currently in the program. Sustainable orthopaedic training can be accomplished in LMICs as demonstrated by the ongoing success of the CURE Kenya Orthopaedic Surgery Residency Program. Additional efforts to expand and replicate this model may assist in providing improved access to high-quality universal healthcare in LMICs.