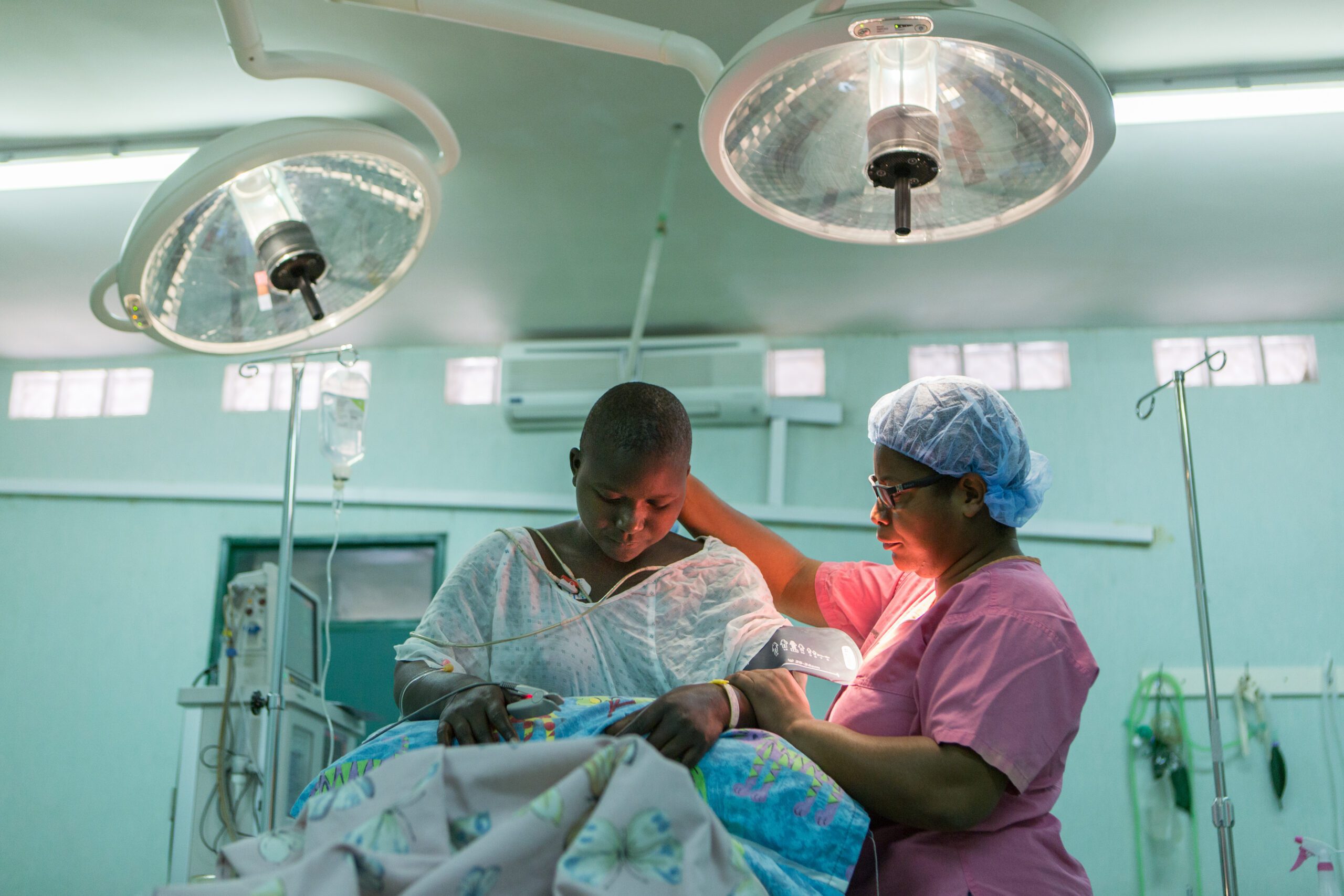
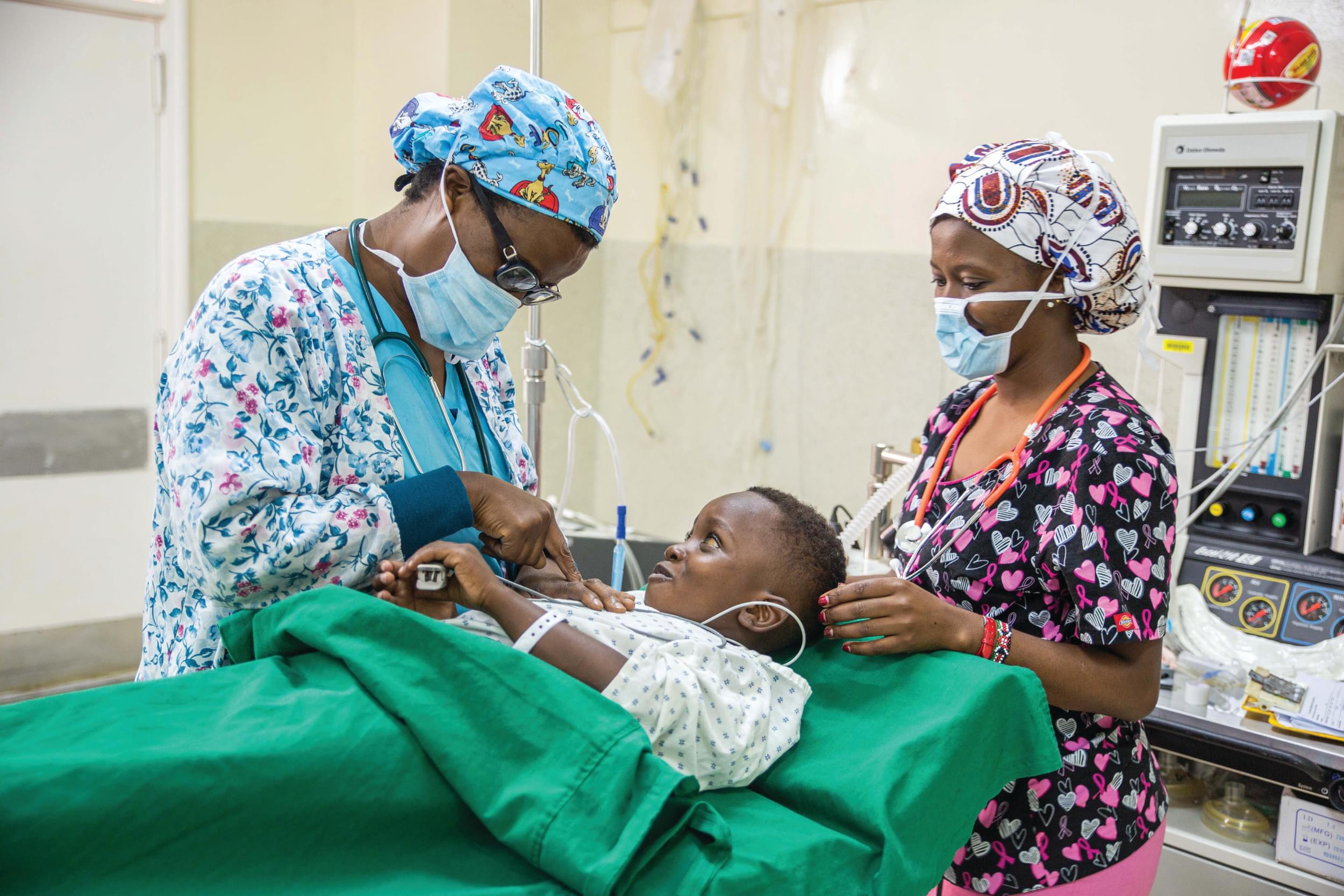
Treatment outcomes of congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia at Beit CURE International Hospital in Blantyre, Malawi
Abstract:
Background: Congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia (CPT) is a rare condition. The natural history of CPT includes persistent instability and progressive deformity. Several CPT treatment methods have been practiced, however, in Africa where there is scarce information on the modalities of treatment available and their outcomes.
Methods: A retrospective cross-sectional study which was conducted among patients with CPT at Beit Cure International Hospital (BCIH), Malawi. Forty-four patients were recruited in this study and their treatment modalities and outcomes were analyzed.
Results: Out of 44 patients recruited in this study, majority (63.6%) were male. The majority of cases were stage 4 congenital tibia pseudarthrosis by Crawford classification. Most patients were treated by more than one surgical modality; however, surgical excision and intramedullary rodding was commonly used (54.7%). The outcomes of treatment were good in 5%, fair in 30%, with amputation in 45% and poor outcomes in 20% of the patients. Complications developed in 60% of patients, predominated by limb length discrepancy. The foot and ankle status were rated by Oxford Foot and Ankle scoring system (OxFAQ).
Conclusions: Congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia is a complex congenital disorder with multiple modalities of treatment. Majority of the patients were treated by more than one operation. Some patients ended up with amputation or poor outcome. Limb length discrepancy, deep infection and pin tract infection are among the common complications.