Total hip replacement surgery in Ethiopia
Abstract:
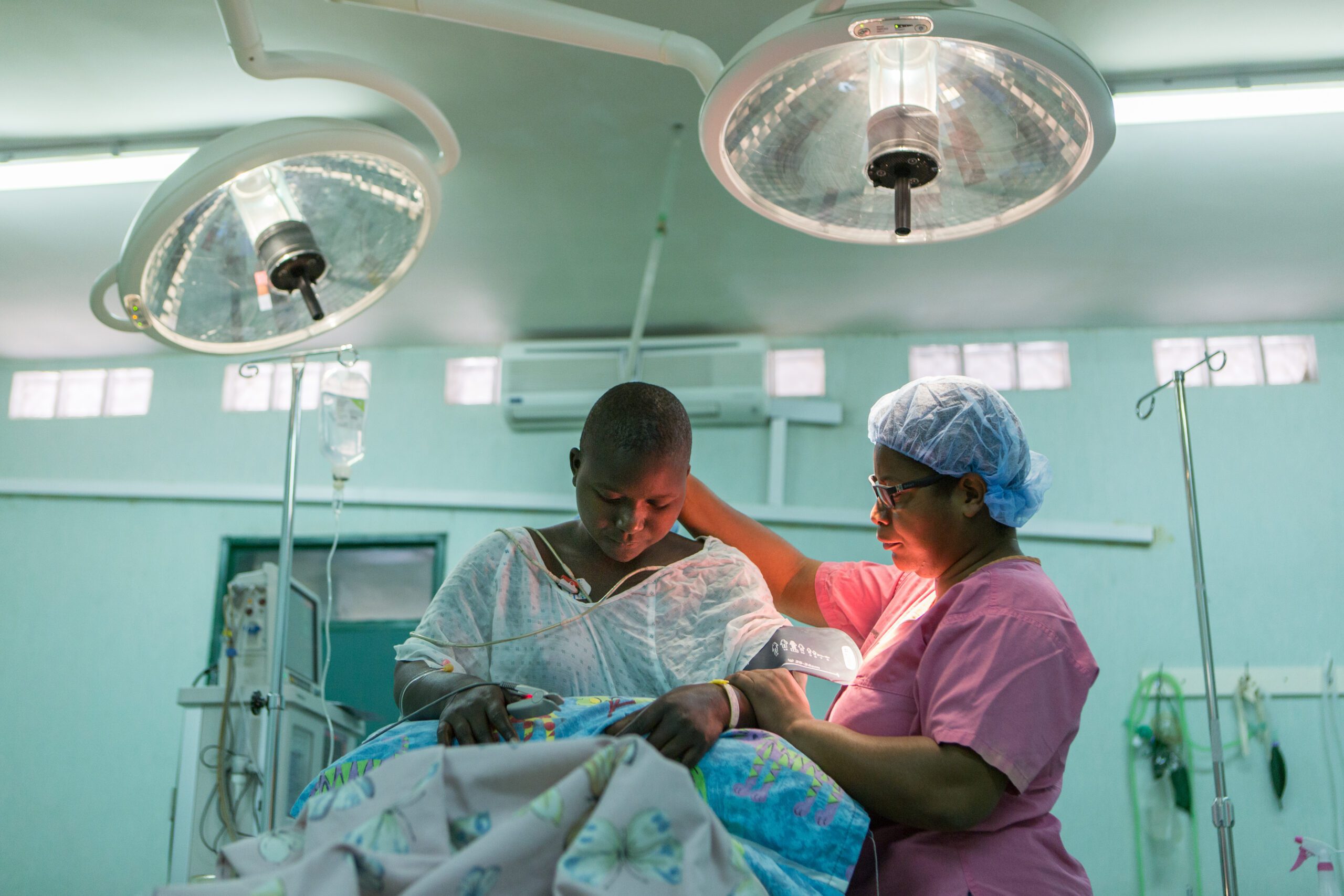
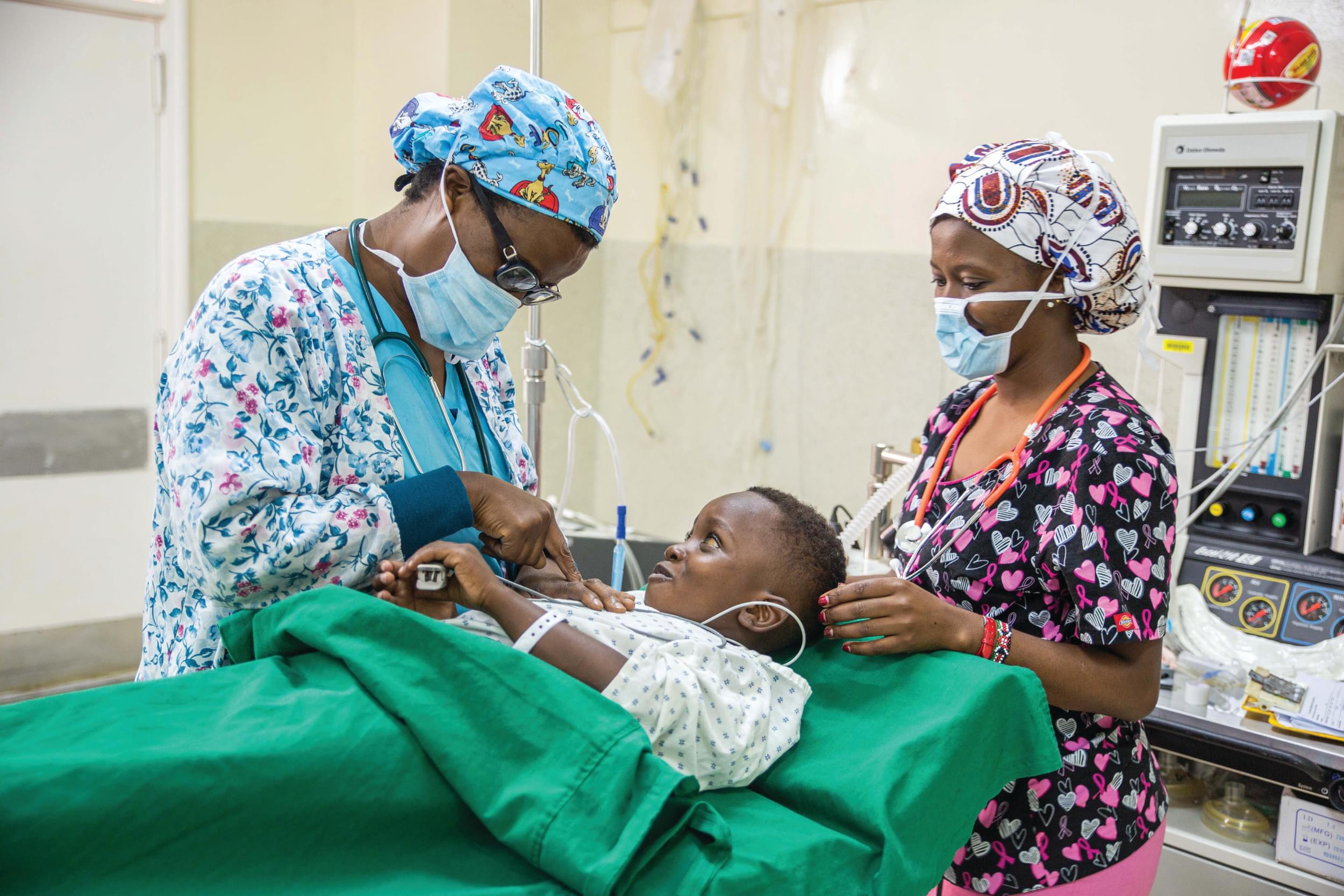
Background: Total hip replacement (THR) surgery has evolved over years to the point that it has been considered as “the operation of the century”. For developed countries, arthroplasty is well established for the management of various joint disorders and has completely revolutionised the treatment of the arthritic hip. The story is different in developing nations. Expensive implant costs and lack of trained orthopaedic surgeons are the main constraints; poverty has caused African countries to remain behind from enjoying the benefits of this medical breakthrough. In this study, we report our first and largest series of 50 such surgeries performed at the CURE Hospital in Addis Ababa. We believe that this is the first consecutive case series from Ethiopia and wanted to share our experience.
Methods: Prospectively, all consecutive patients that underwent THR at CURE Hospital from October 2009 to October 2013 were followed for over 3 years using clinical assessments and hip scores. The hip implant used was a Stryker Omnifit Uncemented HA-coated prosthesis. The Visual Analog Scale (VAS) for pain and the Modified Oxford Hip Score were used to assess outcomes. Variables recorded for each patient included sociodemographic information, diagnosis, comorbidity, surgical approach, duration of surgery, estimated blood loss, implant sizes for Ethiopian hips, complications, sequelae, hip scores, and final patient satisfaction. These were analysed using SPSS version 16. Patterns and learning points were observed.
Results: Of the 50 consecutive THR patients, 26 were male. Mean age was 48 years (range 14-85). In 30 hips, the right side was operated on, and 2 were bilaterally treated. Primary osteoarthritis (OA) and avascular necrosis (AVN) were the leading diagnoses requiring THR. Previous partial hip replacement (PHR, hemiarthroplasty) was converted to THR in 6 patients. The commonest comorbidities were diabetes mellitus and hypertension. There were 4 hips that dislocated after THR and 1 needed revision surgery. There was 1 persistent infection, 1 case of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and 1 death. Mean EBL was approximately 1 L and only 5 patients needed transfusion. The most common sizes for Ethiopian hips were a 28 mm+0 head, 52 mm acetabular shell, and 140 mm #8 stem. The VAS and Modified Oxford Hip scores both improved significantly, and the results were comparable with international standards.
Conclusions: THR is a viable, safe, and effective option in Ethiopia. Appropriate staff training, careful patient selection, continuous supply chain of implants, and establishing a dedicated joint replacement centre will reliably sustain THR surgery.