Effects of honey and sugar dressings on wound healing
Abstract:
Objective: To investigate whether there is a difference between the efficacy of honey and sugar as wound dressings.
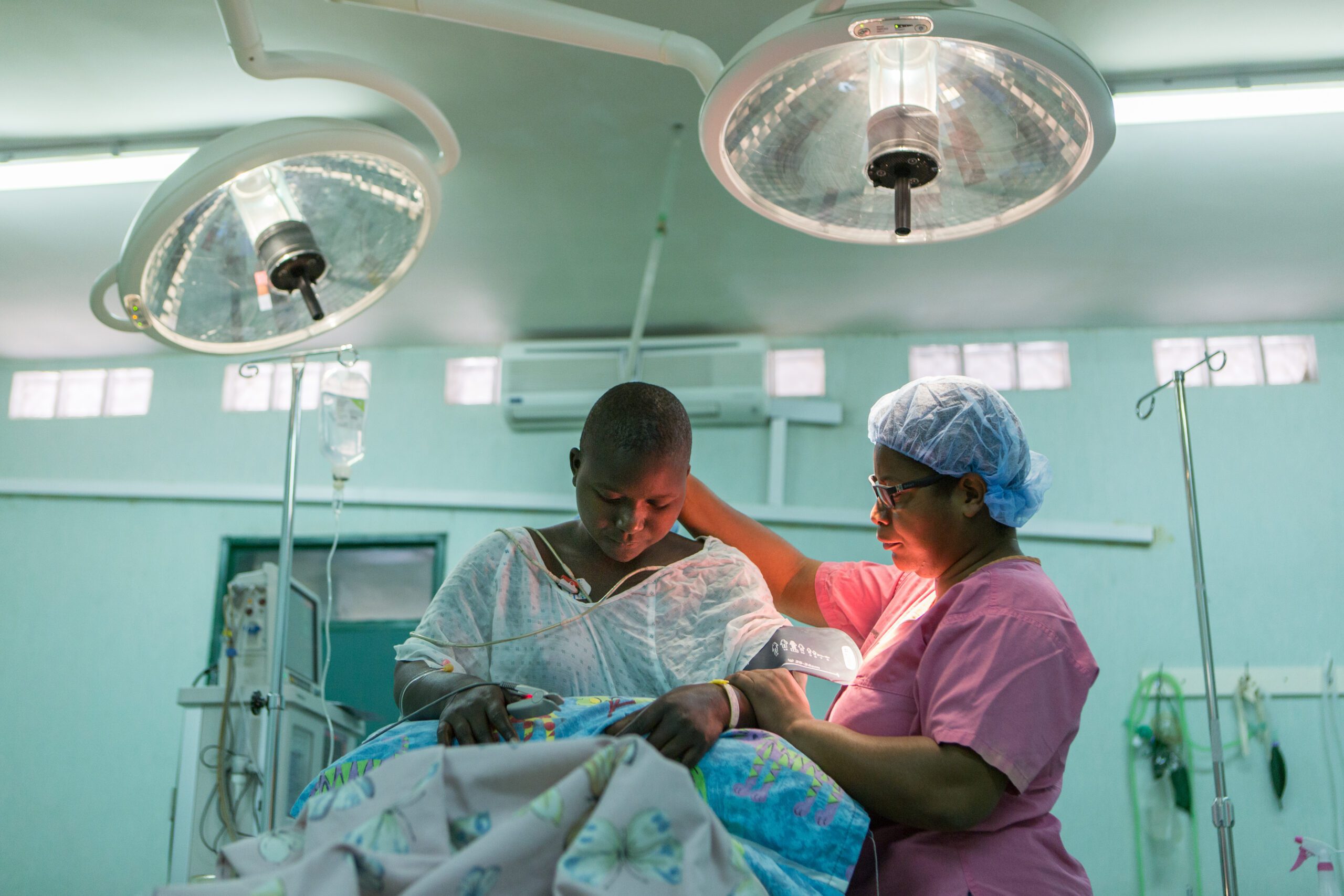
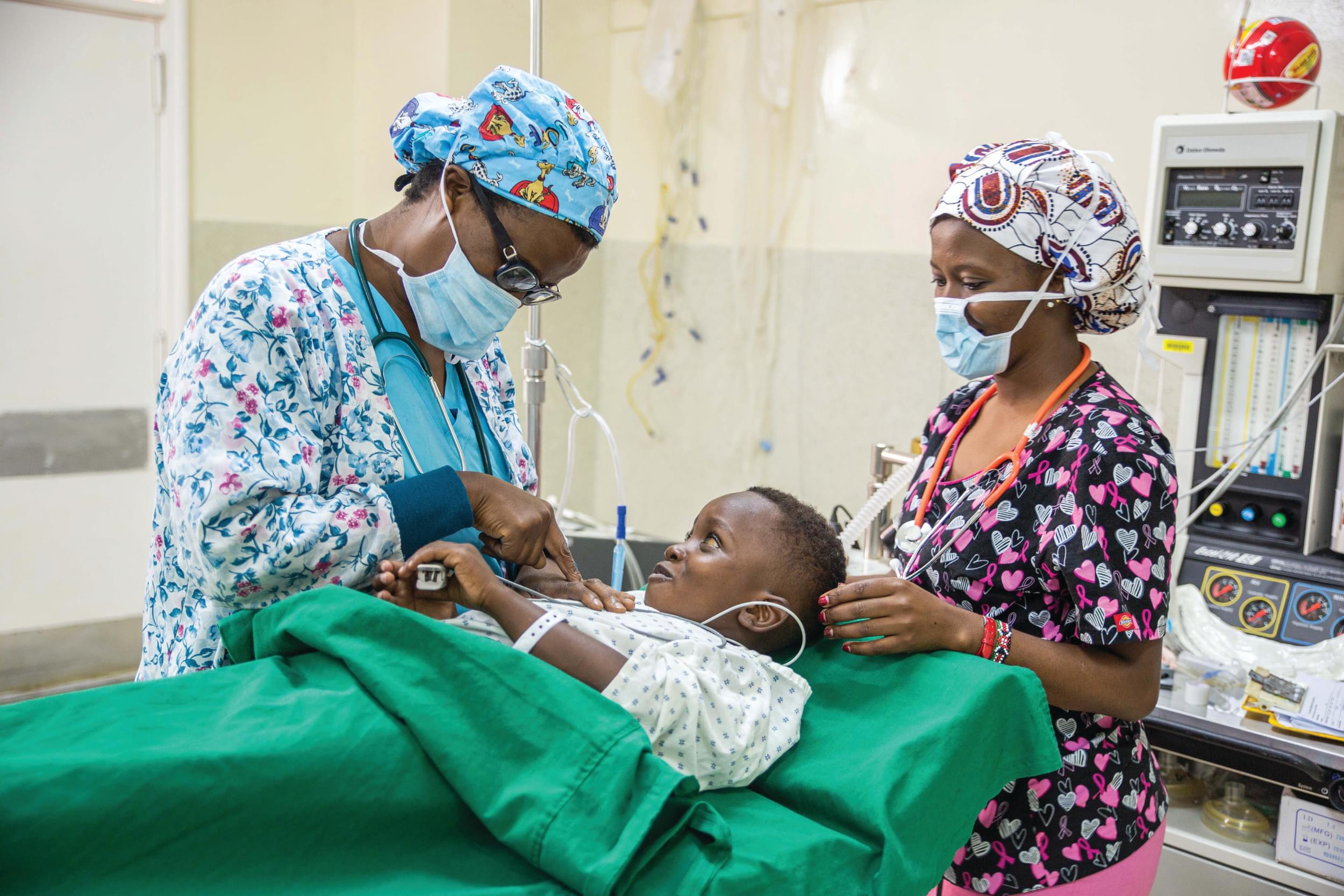
Method: Patients with open or infected wounds were randomised to receive either honey or sugar dressings. Bacterial colonisation, wound size, wound ASEPSIS score and pain were assessed at the start of treatment and at weekly intervals until full healing occurred.
Results: Forty patients were enrolled; 18 received sugar dressings and 22 honey dressings. In the honey group, 55% of patients had positive wound cultures at the start of treatment and 23% at one week, compared with 52% and 39% respectively in the sugar group. The median rate of healing in the first two weeks of treatment was 3.8cm2/week for the honey group and 2.2cm2/week for the sugar group. After three weeks of treatment 86% of patients treated with honey had no pain during dressing changes, compared with 72% treated with sugar.
Conclusion: Honey appears to be more effective than sugar in reducing bacterial contamination and promoting wound healing, and slightly less painful than sugar during dressing changes and motion.